
Efficient Maintenance Management: Work Order Process Flow Chart

Importance of Efficient Maintenance Management
Efficient maintenance management plays a crucial role in organizations, ensuring the smooth operation and extending the lifespan of their equipment. It encompasses various processes and strategies aimed at optimizing maintenance activities, minimizing downtime, and maximizing productivity. A fully functioning work order process flow is one of the key components of efficient maintenance management, enabling streamlined and organized handling of maintenance tasks.
The work order process flow chart provides a visual representation of the steps involved in managing maintenance work orders. It offers a structured approach to handle maintenance requests from submission to completion. This flow chart outlines the sequence of activities, responsibilities, and information necessary for effectively managing work orders throughout their life cycle.
Understanding Maintenance Management
Definition and Objectives of Maintenance Management
Maintenance management refers to the strategic planning, coordination, and control of maintenance activities within an organization. Its primary objectives include ensuring equipment reliability, minimizing downtime, extending equipment life, optimizing resource allocation, and reducing overall maintenance costs. By implementing better work order processes and preventive maintenance work, organizations can enhance operational efficiency and effectively achieve their maintenance goals.
Key Principles of Efficient Maintenance Management
Efficient maintenance management adheres to several key principles that contribute to its effectiveness. These principles include proactive maintenance planning, prioritization based on criticality, regular preventive maintenance work, timely corrective maintenance, accurate documentation, and continuous improvement. By following these principles, organizations can better manage maintenance requests, reduce breakdowns, and improve maintenance efficiency.
Benefits of Effective Maintenance Management
Effective maintenance management offers numerous benefits to organizations. It helps minimize unplanned downtime, improve equipment reliability, extend asset life, enhance safety and compliance, optimize maintenance costs, and increase overall productivity. By implementing work order processes to manage maintenance requests and adopting maintenance management systems, organizations can achieve better asset performance, reduce operational risks, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Work Order Process Flow Chart: An Overview
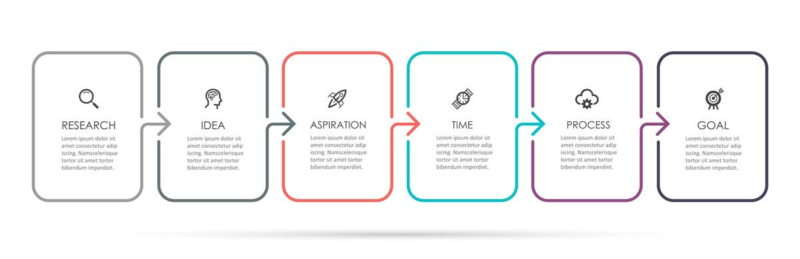
Definition and Purpose of a Work Order
A work order is a document that initiates and tracks maintenance activities. It provides detailed instructions and information regarding the tasks, resources, and timelines required to complete a specific maintenance job. The work order process flow chart outlines the systematic workflow involved in managing work orders, ensuring smooth execution and proper communication throughout the maintenance process.
Components of a Work Order Process Flow Chart
The work order process flow chart typically includes various components. These include submitting a work order request, creating a perfect work order, planning and scheduling, executing and tracking, completing and closing, and reviewing and analyzing. Each component plays a vital role in efficiently managing work orders and contributes to the overall success of maintenance operations.
Importance of Documenting Work Order Processes
Documenting work order processes is crucial for maintaining consistency, ensuring accountability, and facilitating continuous improvement. By documenting each step of the work order process flow, organizations can establish standardized procedures, identify bottlenecks, and implement corrective measures. It also provides a valuable reference for training new employees and serves as a maintenance history for future analysis and evaluation.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Work Order Process Flow Chart

Step 1: Request Initiation
The first step in the work order process flow is initiating a maintenance request. This request can come from various sources, such as employees, equipment operators, or automated monitoring systems. Understanding the source of the work request is crucial for appropriate prioritization and resource allocation.
To initiate a work request, it is necessary to document and gather information. This involves capturing relevant details about the equipment, including its identification number, location, and description of the issue. Gathering comprehensive information facilitates effective planning and execution of the maintenance task.
Step 2: Work Order Creation
Once the maintenance request is initiated, the next step is creating a work order. A work order is a formal document that outlines the specific tasks required to address the maintenance issue. It includes details such as the equipment involved, the nature of the work, and any special instructions or safety considerations.
Creating a perfect work order involves ensuring clarity and comprehensiveness in form and content. The work order form should be user-friendly and capture all the necessary information, such as equipment identification, work order type (preventive, corrective, etc.), and specific procedures or materials required.
Assigning priority and allocating resources is another crucial aspect of work order creation. Prioritizing work orders based on urgency and impact on operations helps in effective resource allocation. The work order should also specify the required resources, such as manpower, tools, and materials, to ensure smooth execution of the maintenance task.
Step 3: Planning and Scheduling
Once the work order is created, the planning and scheduling phase begins. Resource allocation and availability are important considerations at this stage. The maintenance manager needs to assess the availability of skilled technicians, equipment, and materials to schedule the work order efficiently. Proper resource allocation ensures the maintenance task is completed within specified timelines.
Establishing timelines and deadlines is another critical aspect of planning and scheduling. This involves setting realistic timeframes for each task within the work order, considering factors such as the complexity of the job, resource availability, and operational priorities. Clear deadlines help prioritize tasks and maintain accountability throughout the maintenance process.
Step 4: Execution and Tracking
Execution and tracking are essential steps in the work order process flow. Assigning tasks to maintenance personnel is the first aspect of execution. The work order should clearly define the responsibilities of each technician involved, ensuring they have the necessary skills and knowledge to carry out their assigned tasks effectively.
Monitoring progress and updates is equally important during the execution phase. Regular tracking allows the maintenance manager to stay informed about the status of the work order, identify potential delays or issues, and take appropriate actions. It provides an opportunity to address emerging challenges and make necessary adjustments to ensure successful completion of the maintenance task.
Step 5: Completion and Closure
The final step in the work order process flow is completing and closing the work order. This involves conducting quality control and verification to ensure the maintenance task has been performed to the required standards. It may include inspections, tests, or sign-offs from authorized personnel to validate the completion of the work.
Documenting the work performed is essential for future reference and analysis. This includes recording details such as completed tasks, materials used, time spent on the project, and any additional notes or observations. Proper documentation helps maintain a maintenance history, facilitates better decision-making, and enhances future maintenance processes.
Incorporating work order software in the process can greatly streamline these steps. Work order software automates and digitizes the workflow, reducing reliance on manual processes and paper. It enables efficient tracking of work orders, provides instant notifications to requesting users about changes or progress, and helps better manage maintenance requests, processes, and historical data.
By following a well-defined work order process flow chart and incorporating modern maintenance management systems, organizations can optimize their maintenance operations, improve resource utilization, and achieve better equipment reliability. The step-by-step breakdown outlined above, along with the effective use of work order software, contributes to a seamless and efficient maintenance management approach.
Benefits of Implementing the Work Order Process Flow Chart
Improved efficiency and productivity
Implementing a well-defined work order process flow chart brings numerous benefits to maintenance management. One of the key advantages is improved efficiency and productivity. By following a structured flow, organizations can streamline their maintenance operations and reduce downtime. Properly documented work orders ensure technicians have all the necessary information to carry out their tasks efficiently, minimizing delays and maximizing productivity. The use of work order software also facilitates scheduling and tracking, allowing for better allocation of resources and time management.
Enhanced communication and coordination
The work order process flow chart promotes better communication and coordination within the maintenance team. Clear and standardized work orders facilitate effective communication between maintenance personnel, supervisors, and requesting users. Everyone involved has access to the same information, reducing the chances of miscommunication or misunderstandings. This leads to improved collaboration and coordination, resulting in smoother maintenance processes. Work order software also enables instant notifications to requesting users, keeping them informed of any changes or updates, which further enhances communication and coordination.
Minimized downtime and disruptions
Efficient work order management helps minimize downtime and disruptions to operations. By promptly addressing maintenance requests and following a structured process, organizations can identify and resolve equipment issues before they lead to major breakdowns. Emergency work orders can be prioritized and handled swiftly to minimize the impact on operations. Preventive maintenance work orders, such as routine maintenance, can be scheduled and executed in a timely manner, ensuring equipment remains in optimal condition and reducing the likelihood of unexpected failures. Proper planning and resource allocation, facilitated by the work order process flow chart and work order software, help minimize the disruption caused by maintenance activities.
Accurate data tracking and reporting
Implementing a work order process flow chart allows for accurate data tracking and reporting. Each work order represents a part of the maintenance history, documenting the work performed, materials used, and time spent on each project. This information is crucial for generating comprehensive reports and analysis. Organizations can track the time spent on a project, including labor hours and materials used, enabling accurate cost analysis and resource allocation. Work order software also facilitates the recording and tracking of data, ensuring accurate and up-to-date information for reporting purposes.
Incorporating work order software and utilizing different types of work orders, including emergency work orders and routine maintenance, helps facilities management in better managing maintenance requests and processes. Additionally, the use of purchase orders can streamline procurement processes, ensuring the availability of necessary materials for maintenance tasks. By implementing a well-defined work order process flow chart and leveraging work order software, organizations can optimize their maintenance operations, improve resource utilization, and achieve better equipment reliability.
Challenges and Best Practices in Work Order Management
Common challenges in implementing work order processes

Implementing work order processes can pose several challenges that organizations need to address to ensure successful adoption. Some of the common challenges include:
- Resistance to change: Maintenance staff who are accustomed to traditional methods, such as using pen and paper or manual processes, may resist the transition to work order systems. Overcoming this challenge requires effective change management strategies, such as clear communication, training, and emphasizing the benefits of the new system, to help employees understand the value and efficiency of the new processes.
- Lack of standardized work order templates or documentation: Inconsistent or unclear work order templates and documentation can hinder the effectiveness of the work order process. It is important to develop standardized templates that capture all necessary information for each type of work order. Clear instructions and standardized formats help ensure consistency, clarity, and ease of understanding for all stakeholders involved in the process.
- Difficulties in accurately tracking time and materials spent on projects: Accurate tracking of time and materials spent on projects is crucial for effective maintenance management. However, manually tracking this information can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Adopting technology-driven solutions, such as work order management software or mobile applications, can simplify and automate the tracking process. These tools enable technicians to log their time and materials digitally, ensuring accuracy and providing real-time data for analysis and reporting.
- Managing the work order life cycle: The work order life cycle involves various stages, including creation, assignment, execution, review, and closure. Managing the entire life cycle can be complex, especially when multiple work orders are in progress simultaneously. Effective work order management systems are needed to ensure smooth coordination, visibility, and accountability throughout the process. Automation and workflow management tools can help streamline the work order life cycle, ensuring efficient progress and timely completion of tasks.
- Using work orders to schedule and manage equipment maintenance: Efficient scheduling and management of equipment maintenance is crucial to prevent breakdowns and maximize uptime. Work orders play a vital role in this process by facilitating the scheduling of preventive maintenance, inspections, repairs, and replacements. However, it can be challenging to prioritize work orders, allocate resources, and balance maintenance activities with operational requirements. Effective planning, prioritization techniques, and the use of maintenance management software can help optimize scheduling and resource allocation, ensuring equipment maintenance is conducted in a timely and efficient manner.
Best practices for efficient work order management

To ensure efficient work order management, organizations can follow several best practices:
1. Utilizing technology and software solutions: Implementing work order software streamlines the entire process, automates data tracking, and improves communication. It enables technicians to submit work orders electronically, tracks labor allocation, and instantly notifies requesting users of any changes or updates.
2. Training and empowering maintenance staff: Providing training on the work order process flow and the use of software tools empowers maintenance staff to effectively manage and execute work orders. Proper training ensures technicians understand the importance of following the process, accurately documenting their work, and utilizing technology to enhance productivity.
By embracing these best practices, organizations can overcome challenges, improve their work order management, and achieve more efficient and effective maintenance operations.
In conclusion, implementing a well-defined work order process flow chart brings numerous benefits to maintenance management, including improved efficiency, enhanced communication, minimized downtime, and accurate data tracking. Overcoming challenges and following best practices, such as utilizing technology and empowering staff, ensures organizations can optimize their work order management and achieve better maintenance outcomes.
More Information
Field Service Software: Streamlining Operations for Small Businesses
Field Service Software is revolutionizing the way small businesses in various industries manage their operations. With its ability to streamline and optimize field service operations, this technology solution has become a game-changer for businesses like HVAC, Appliance Repair, Chimney Sweep, Cleaning Business, Contractor Business, Electrician Business, Handyman, and Plumbing.
Enhancing Efficiency with Field Service Software
Field Service Software, such as ServiceFolder, offers a comprehensive set of tools and features that enable businesses to efficiently manage their daily operations. From scheduling and dispatching to inventory management and invoicing, this online software solution simplifies complex processes, saving businesses valuable time and resources. By automating manual tasks and providing real-time data, it helps businesses make informed decisions and deliver exceptional service to their customers.
Insights from Field Service Management Blog
ServiceFolder takes pride in providing valuable insights and information through their Field Service Management Blog. With a wide range of topics covered, businesses in the field service industry can gain valuable knowledge and stay up-to-date with the latest trends and best practices. Some of the informative blogs include:
- Efficient Order Management Through Sales Order Process Flowchart
- Field Service Software vs CMMS Service: Differences and Benefits
- Mastering Order Management Process Flow Chart and Best Practices
- Optimizing Your Business with an Order Fulfillment Process Flow Chart
Transforming Industries with Field Service Software
Field Service Software is not limited to specific industries. It has the potential to transform various sectors. ServiceFolder explores how this technology is changing industries such as the trucking industry, non-profit organizations, and agriculture in their informative blog posts:
- How FSM is Changing the Trucking Industry
- How FSM is Helping Non-Profit Organizations
- How FSM Software is Boosting Agriculture Efficiency
Leveraging SEM and SEO for Field Service Businesses
In the highly competitive field service industry, businesses need to leverage digital marketing strategies to gain a competitive edge. ServiceFolder highlights the importance of Search Engine Marketing (SEM) and Search Engine Optimization (SEO) in their blog post:
Embrace the Power of Service Management Software
To stay ahead in the field service industry, businesses must embrace the power of Service Management Software. ServiceFolder offers a robust software solution that enabl* Closing connection 0
- schannel: shutting down SSL/TLS connection with api.openai.com port 443 es businesses to streamline their operations, improve customer satisfaction, and drive growth. Learn more about their Service Management Software here.
Streamlining Field Service Operations with RFID Technology
The integration of Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is revolutionizing field service operations. ServiceFolder explores the benefits of streamlining field service management with RFID technology here.
In conclusion, Field Service Software is a game-changer for small businesses in the field service industry. With its ability to streamline operations, provide valuable insights, and transform industries, it is a must-have technology solution for businesses looking to thrive in today’s competitive landscape.
Related Posts
Try Now
ServiceFolder's field service scheduling software free plan is perfect for small businesses with up to three people or less. It includes time tracking, scheduling, and mobile app features that make it one of the best mobile field service management software solutions for small businesses available. It is perfect for any small business company within the field service industry that wants to use technology to increase performance and productivity.